Mastering SSH Tunneling On Raspberry Pi: A Comprehensive Guide
SSH tunneling on a Raspberry Pi is a powerful tool for securing your network connections and accessing remote systems securely. Whether you're a hobbyist, a developer, or someone who simply loves tinkering with technology, understanding how to set up and use SSH tunnels can open up a world of possibilities. From remote access to encrypted data transfer, the Raspberry Pi, combined with SSH tunneling, offers a cost-effective and versatile solution for managing your digital infrastructure.
For those unfamiliar, SSH tunneling allows you to create a secure connection between your Raspberry Pi and another system over an unsecured network. This process encrypts your data, ensuring that sensitive information remains private. With the Raspberry Pi's compact size and low power consumption, it's an ideal device for setting up secure tunnels in environments ranging from home networks to enterprise setups. The combination of SSH tunneling and Raspberry Pi can be used for tasks like remote desktop access, secure browsing, and even bypassing restrictive firewalls.
As we dive deeper into this article, you'll discover the ins and outs of SSH tunneling on Raspberry Pi, including step-by-step instructions, practical use cases, and troubleshooting tips. Whether you're new to the world of Raspberry Pi or an experienced user looking to expand your knowledge, this guide will equip you with the tools and insights needed to harness the full potential of SSH tunneling. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of how to implement this technology and why it's such a valuable skill in today's digital landscape.
- Is Tyler Childers Still Married
- P Diddys Children
- Nail Designs For Almond Shape Nails
- Houston Dynamo Vs Columbus Crew Lineups
- Marie Temara Net Worth
Table of Contents
- What is SSH Tunneling and Why Use It on a Raspberry Pi?
- How Does SSH Tunneling Work on a Raspberry Pi?
- Step-by-Step Guide: Setting Up SSH Tunneling on Raspberry Pi
- What Are the Practical Use Cases for SSH Tunneling Raspberry Pi?
- Troubleshooting Common Issues with SSH Tunneling Raspberry Pi
- What Are the Best Security Practices for SSH Tunneling Raspberry Pi?
- Advanced Configurations and SSH Tunneling Raspberry Pi
- Frequently Asked Questions About SSH Tunneling Raspberry Pi
What is SSH Tunneling and Why Use It on a Raspberry Pi?
SSH tunneling, also known as SSH port forwarding, is a method of creating a secure connection between two systems over an unsecured network. This process involves encapsulating other network protocols within an SSH connection, ensuring that all data transmitted is encrypted and protected from eavesdropping or tampering. The Raspberry Pi, with its compact design and versatility, serves as an excellent platform for implementing SSH tunneling. Its ability to run continuously with minimal power consumption makes it an ideal choice for both personal and professional use cases.
So, why should you consider using SSH tunneling on a Raspberry Pi? First and foremost, it enhances security. By encrypting your data, SSH tunneling protects sensitive information such as login credentials, file transfers, and remote commands from being intercepted. This is particularly important when accessing your Raspberry Pi over public Wi-Fi networks, where the risk of cyberattacks is higher. Additionally, SSH tunneling allows you to bypass restrictive firewalls and access services that might otherwise be blocked. For example, you can securely access your home network or a private server from anywhere in the world.
Another compelling reason to use SSH tunneling on a Raspberry Pi is its versatility. Whether you're a developer looking to securely deploy applications, a hobbyist setting up a home automation system, or a business professional managing remote servers, SSH tunneling can meet your needs. It also supports a variety of use cases, from remote desktop access to encrypted web browsing. By leveraging the Raspberry Pi's capabilities, you can create a robust and cost-effective solution for managing your digital infrastructure securely.
How Does SSH Tunneling Work on a Raspberry Pi?
To understand how SSH tunneling works on a Raspberry Pi, let's break it down into simple terms. At its core, SSH tunneling involves creating a secure "tunnel" between your Raspberry Pi and another system. This tunnel encrypts all data passing through it, ensuring that your information remains private and secure. The process begins when you establish an SSH connection from your local machine to the Raspberry Pi. Once the connection is established, you can configure the tunnel to forward specific ports, allowing you to access services securely.
Types of SSH Tunneling
There are three main types of SSH tunneling: local, remote, and dynamic. Each type serves a different purpose, depending on your needs:
- Local Port Forwarding: This type allows you to forward traffic from a port on your local machine to a port on the Raspberry Pi. It's commonly used to access services running on the Raspberry Pi from your local machine securely.
- Remote Port Forwarding: In this scenario, traffic from a port on the Raspberry Pi is forwarded to a port on your local machine. This is useful when you want to expose a local service to the internet securely.
- Dynamic Port Forwarding: This type creates a SOCKS proxy, allowing you to route traffic dynamically through the Raspberry Pi. It's ideal for secure browsing and bypassing firewalls.
What Are the Key Components of SSH Tunneling Raspberry Pi?
Several key components work together to make SSH tunneling on a Raspberry Pi possible:
- SSH Client: This is the software you use to initiate the SSH connection. Popular SSH clients include OpenSSH, PuTTY, and MobaXterm.
- SSH Server: The Raspberry Pi runs an SSH server, which listens for incoming connections and manages the tunnel.
- Ports: Ports are used to direct traffic through the tunnel. You'll need to specify the source and destination ports when setting up the tunnel.
- Encryption: SSH tunneling uses strong encryption algorithms to protect your data from unauthorized access.
By understanding these components and how they interact, you can effectively set up and manage SSH tunnels on your Raspberry Pi. This knowledge will empower you to create secure connections for a wide range of applications.
Step-by-Step Guide: Setting Up SSH Tunneling on Raspberry Pi
Setting up SSH tunneling on a Raspberry Pi is a straightforward process, but it requires careful attention to detail. Below, we'll walk you through the steps to configure local, remote, and dynamic port forwarding. By following these instructions, you'll be able to establish secure connections for various use cases, from remote access to encrypted browsing.
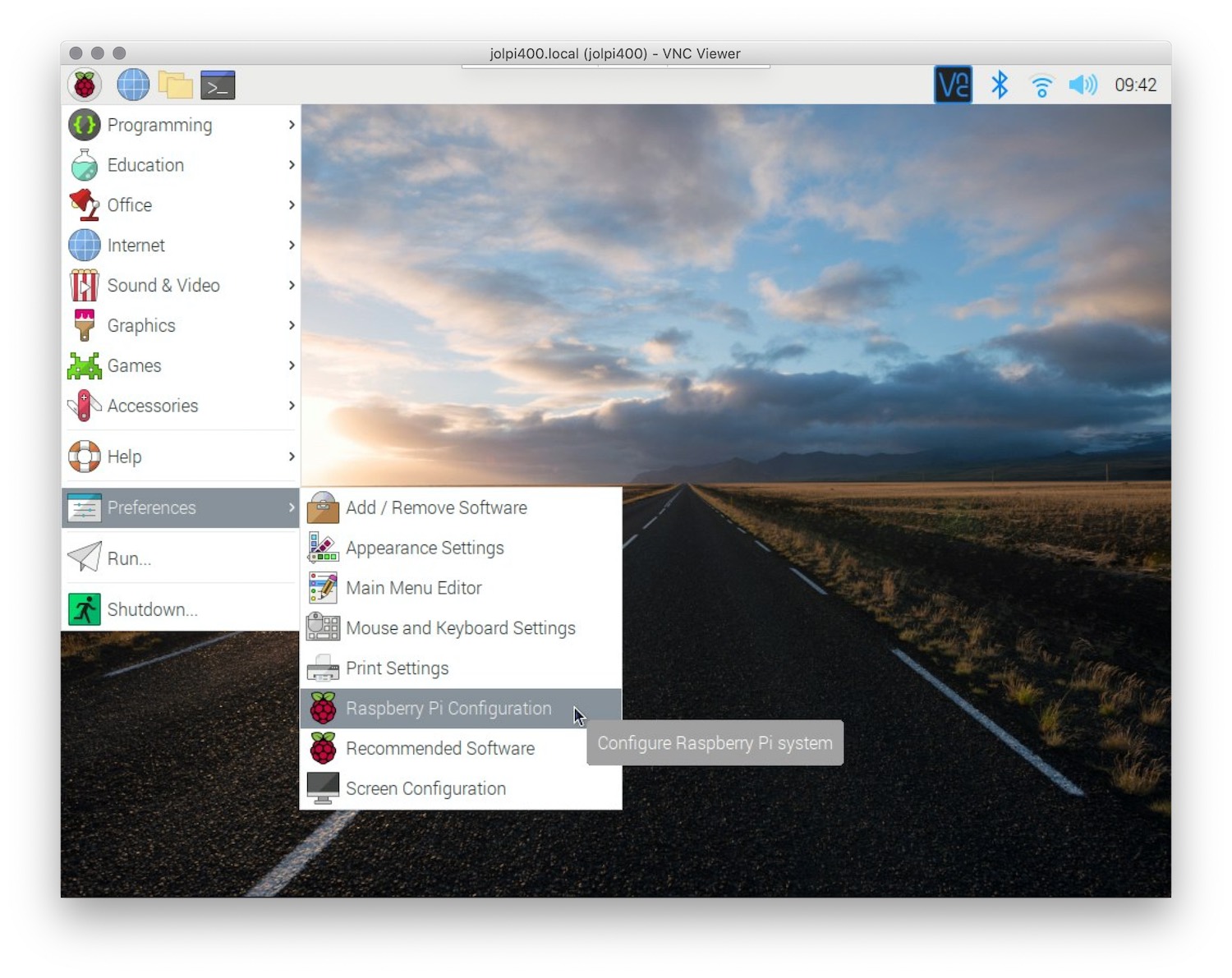
Step 1: Enable SSH on Your Raspberry Pi
Before you can start tunneling, you need to ensure that SSH is enabled on your Raspberry Pi. Here's how:
- Open the terminal on your Raspberry Pi or connect to it via SSH.
- Type
sudo raspi-configand press Enter. - Navigate to "Interfacing Options" and select "SSH."
- Choose "Yes" to enable SSH and exit the configuration tool.
Once SSH is enabled, you can connect to your Raspberry Pi from another machine using its IP address.
Step 2: Set Up Local Port Forwarding
Local port forwarding allows you to securely access services running on your Raspberry Pi. Here's how to set it up:
- Open your SSH client and connect to the Raspberry Pi using the command:
ssh -L [local_port]:[destination_ip]:[destination_port] [username]@[raspberry_pi_ip] - Replace
[local_port],[destination_ip], and[destination_port]with the appropriate values for your setup. - Once connected, you can access the service by navigating to
localhost:[local_port]on your local machine.
Step 3: Configure Remote Port Forwarding
Remote port forwarding is useful for exposing local services to the internet. Follow these steps:
- Use the command:
ssh -R [remote_port]:[local_ip]:[local_port] [username]@[raspberry_pi_ip] - Replace the placeholders with the correct values for your configuration.
- After establishing the connection, the Raspberry Pi will forward traffic from its
[remote_port]to your local machine's[local_port].
Step 4: Create a Dynamic SOCKS Proxy
Dynamic port forwarding creates a SOCKS proxy, enabling secure browsing and bypassing firewalls:
- Use the command:
ssh -D [local_port] [username]@[raspberry_pi_ip] - Configure your browser or application to use
localhost:[local_port]as a SOCKS proxy. - All traffic routed through the proxy will be encrypted and forwarded via the Raspberry Pi.
By following these steps, you can successfully set up SSH tunneling on your Raspberry Pi and begin leveraging its capabilities for secure communication and data transfer.
What Are the Practical Use Cases for SSH Tunneling Raspberry Pi?
SSH tunneling on a Raspberry Pi opens up a wide range of practical applications, making it an invaluable tool for both personal and professional use. Below, we'll explore some of the most common and innovative use cases, highlighting how this technology can enhance security, accessibility, and efficiency in various scenarios.
1. Secure Remote Access to Home Networks
One of the most popular uses of SSH tunneling on a Raspberry Pi is to securely access your home network from anywhere in the world. By setting up a tunnel, you can remotely manage devices, access files, and even control smart home systems without exposing them to the public internet. For instance, you can use SSH tunneling to securely access a home server running on your Raspberry Pi, ensuring that your data remains private and protected from unauthorized access.
2. Bypassing Restrictive Firewalls
In environments where internet access is restricted, such as corporate networks or public Wi-Fi hotspots, SSH tunneling can help you bypass these limitations. By creating a dynamic SOCKS proxy, you can route your web traffic through the Raspberry Pi, effectively circumventing firewalls and accessing blocked websites. This is particularly useful for developers and IT professionals who need unrestricted access to online resources while traveling or working in restrictive environments.
What Are Some Advanced Use Cases for SSH Tunneling Raspberry Pi?
Beyond the basics, SSH tunneling on a Raspberry Pi can be used for more advanced applications, such as:
- Remote Desktop Access: Use SSH tunneling to securely access your Raspberry Pi's desktop environment from another machine, enabling remote management and troubleshooting.
- Encrypted File Transfers: Securely transfer files between your Raspberry Pi and other systems by tunneling protocols like SFTP or SCP through SSH.
- IoT Device Management: In IoT setups, SSH tunneling can be used to securely manage and monitor connected devices, ensuring that sensitive data remains protected.
These use cases demonstrate the versatility and power of SSH tunneling on a Raspberry Pi, making it a valuable tool for anyone looking to enhance their digital infrastructure's security and functionality.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with SSH Tunneling Raspberry Pi
While SSH tunneling on a Raspberry Pi is a powerful tool, it can sometimes present challenges that require troubleshooting. Below, we'll explore some common issues users encounter and provide practical solutions to help you resolve them efficiently.
1. Connection Refused Errors
One of the most frequent issues is the "connection refused" error, which typically occurs when the Raspberry Pi's SSH service is not running or the port is blocked. To resolve this:
- Ensure that SSH is enabled on your Raspberry Pi by running
sudo systemctl status ssh. If it's not active, start the service usingsudo systemctl start ssh. - Check your firewall settings to ensure that the SSH port (default is 22) is open and not blocked by any rules.
- Verify that you're using the correct IP address for your Raspberry Pi and that it's reachable on the network.
2. Slow or Unresponsive Tunnels
If your SSH tunnel feels slow or unresponsive, the issue may be related to
Article Recommendations
- The Jeffersons Cast Dead Or Alive
- Richardsons Ice Cream Flavors
- Best Memes From Debate
- Northfield Newspaper
- Chesapeake Inn Marina

Detail Author:
- Name : Conner Jacobi
- Username : madaline71
- Email : igoldner@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 1970-09-07
- Address : 87818 Aliza Summit South Lilyan, PA 60315-2757
- Phone : +13612364056
- Company : Monahan-Weissnat
- Job : Conveyor Operator
- Bio : Dolorem ad voluptatem laudantium eos quia. Sit repellat necessitatibus laboriosam sint. Eum est qui qui animi.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/feest1994
- username : feest1994
- bio : Velit voluptatem libero sint enim aspernatur rem culpa.
- followers : 779
- following : 2604
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/tyrese.feest
- username : tyrese.feest
- bio : Aliquam illum voluptas et deserunt. Pariatur aliquid illo cupiditate et. Repudiandae modi rerum sit dignissimos itaque nam.
- followers : 6606
- following : 2639
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@tfeest
- username : tfeest
- bio : Dicta sint eos libero non. Ut quidem dolor et saepe omnis eos et.
- followers : 421
- following : 1118